Obesity
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 24, 2023.
What is Obesity?

Obesity is an excess of body fat.
It is difficult to directly measure body fat. Body mass index (BMI) is a popular method of defining a healthy weight. BMI should be used as a guide, along with waist size, to help estimate the amount of body fat.
BMI estimates a healthy weight based on your height. Because it considers height as well as weight, it is a somewhat better guide than body weight alone.
To calculate your BMI:
- Multiply your weight in pounds by 703.
- Divide that answer by your height in inches.
- Divide that answer by your height in inches again.
Then use the chart below to see what category your BMI falls into.
|
BMI |
Category |
|
Below 18.5 |
Underweight |
|
18.5 – 24.9 |
Healthy |
|
25.0 – 29.9 |
|
|
30.0 – 39.9 |
Obese |
|
Over 40 |
Morbidly obese |
Obesity can shorten your life. It can also put you at risk of developing a number of conditions. These include:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Some forms of cancer.
Many other health risks are higher for people who are obese. These risks may increase as the degree of obesity increases.
Where you carry the extra weight is also important. People who carry extra weight around their waist may be more likely to experience health problems caused by obesity than those who carry it in their legs and thighs.
People become obese for a number of reasons. Often, several of these factors are involved.
Some of the most common reasons for obesity are:
- Genetic influences: Your genetic makeup plays a significant role in your chances of becoming obese. However, you still maintain most of the control when it comes to your weight. Some rare genetic diseases make it almost impossible to avoid obesity.
- Physiological influences: Some researchers believe that every person has a predetermined weight that the body resists moving away from. Also, people of the same age, sex and body size often have different metabolic rates. This means their bodies burn food differently. Someone with a low metabolic rate may require fewer calories to maintain approximately the same weight as someone whose metabolic rate is high.
- Food intake and eating disorders: If you eat a lot, especially foods that are high in fat and calories, you can become obese. Obesity also can result from eating disorders, such as a tendency to binge.
- Lifestyle: If you lead a sedentary lifestyle, you are at a higher risk of becoming obese.
- Your weight history: If you were overweight as a child or adolescent, you are more likely to be obese as an adult.
- Drugs: Some drugs can cause obesity. These include steroid hormones and many drugs used to treat psychiatric conditions.
Symptoms
The primary warning sign of obesity is an above-average body weight. If you are obese, you may also experience:
- Trouble sleeping
- Sleep apnea (a condition in which breathing is irregular and periodically stops during sleep)
- Shortness of breath
- Varicose veins
- Skin problems caused by moisture that accumulates in the folds of your skin
- Gallstones
- Osteoarthritis in weight-bearing joints, especially the knees.
Obesity increases your risk for:
- High blood pressure
- High levels of blood sugar (diabetes)
- High cholesterol
- High triglycerides levels.
Diagnosis
Obesity is diagnosed by calculating your BMI. BMI is based on your height and weight. A BMI of 30 or more defines obesity. In general, this means your body weight is 35% to 40% more than your ideal body weight.
Your body fat also can be calculated by using skin calipers. Calipers are an instrument that measures the thickness of your skin.
Body shape is also important. People who carry most of their weight around the waist (apple shaped) have a greater risk of heart disease and diabetes than do people with big hips and thighs (pear shaped).
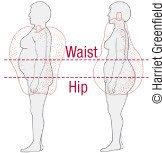
Waist circumference is a good measure of abdominal obesity. Ideally your waist size should be no more than one-half of your height. Women with a waist more than 35 inches or men with a waist more than 40 inches are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, fatty liver and type 2 diabetes.
Expected duration
Obesity is often a lifelong problem. Once excess weight is gained, it is not easy to lose. Once lost, you will have to work at maintaining your healthier weight.
The length of time it takes to reach your weight goal depends on:
- How much you have to lose
- Your activity level
- The type of treatment or weight-loss program you choose.
Diseases and conditions caused by obesity often improve as you lose weight.
Prevention
To prevent obesity and maintain a healthy body weight, eat a well-balanced diet and exercise regularly.
Preventing obesity is important. Once fat cells form, they remain in your body forever. Although you can reduce the size of fat cells, you cannot get rid of them.
Treatment
Weight reduction is achieved by:
- Consuming fewer calories
- Increasing activity and exercise.
Structured approaches and therapies to reduce weight include:
- A modified diet. A reasonable weight loss goal is 1 to 2 pounds per week. This can usually be achieved by eating 500 to 1,000 fewer calories each day. Whether you concentrate on eating less fat or fewer carbohydrates is up to you. Fats have more than twice as many calories per ounce than carbohydrates or protein. If you cut out carbohydrates, you still need to limit fat intake. Choose healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated oils.
- Regular exercise. To effectively lose weight, most people need to do moderate intensity exercise for 60 minutes most days of the week. Add more activity during the day. Take the stairs and get up often from your desk or sofa.
- Non-prescription orlistat (Alli). Orlistat inhibits fat absorption in the intestine. Originally, this medication was only available by prescription (Xenical). The over-the-counter medicine is sold at a lower dose than Xenical. But the active ingredient is the same.
- Other non-prescription diet pills. Over-the-counter diet pills often contain ingredients that can increase heart rate and blood pressure. It is not clear how effective they are in producing weight loss that can be maintained over time. Common side effects include feeling jittery and nervous and having heart palpitations. Some experts believe they may be associated with an increased risk of stroke.
- Prescription medications. To help you lose weight, your doctor may prescribe medications along with a calorie-restricted diet. Almost all people regain weight when they stop using these medications.
- Surgery. In general, weight-loss surgery (called bariatric surgery) may be considered if your BMI is 40 or greater, or your BMI is 30-35 or greater and you have at least one medical condition directly related to obesity. In addition, you must have participated in a structured weight loss program without success.
Types of surgical procedures include:
- Gastroplasty – also known as stomach stapling. A surgeon creates a small pouch in the stomach that allows only limited amounts of food to be eaten at one time.
- Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. A surgeon places an adjustable band around the stomach with minimally invasive surgery.
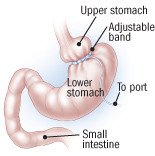
- Gastric bypass. This is the most effective weight loss surgery. However, it also carries a greater risk of complications, both short term and long term. A surgeon creates a small pouch in the upper part of the stomach. A hole is made in the small intestine beyond the normal stomach attachment. The pouch is attached to the hole, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the top part of the small intestine.
When to call a professional
Call your doctor if you need help losing weight. Also call if you have any of the symptoms or complications of obesity.
Prognosis
Others, however, find it difficult to maintain the weight loss for long. Most people return to their pretreatment weight within five years.
Additional info
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics
https://www.eatright.org/
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/
Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition
https://www.fda.gov/Food/default.htm
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
